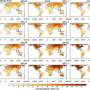
A recent study has found that global warming is significantly intensifying day-to-day temperature fluctuations, creating a new climate hazard with serious implications for human health. This increasing volatility leads to more extreme shifts in temperature, resembling a “climate roller coaster” effect, that poses risks to communities around the world.
The research highlights that these rapid temperature changes are no longer anomalies but rather a growing trend linked to climate change. According to the study published on October 10, 2023, in the journal *Nature Climate Change*, the frequency of extreme temperature swings has escalated, affecting not only weather patterns but also public health.
Impact on Human Health and Daily Life
The study identifies that populations are becoming increasingly vulnerable to health issues resulting from these fluctuations. The health sector warns that more frequent exposure to temperature extremes can lead to conditions such as heat stress, respiratory problems, and other climate-related illnesses.
For example, individuals with pre-existing health conditions may experience exacerbated symptoms during these extreme temperature events. Furthermore, the stress on healthcare systems could escalate, particularly in regions already facing challenges related to public health infrastructure.
Researchers noted that the “climate roller coaster” effect is particularly pronounced in urban areas, where heat islands can amplify temperature extremes. This phenomenon can lead to significant disparities in health outcomes, as marginalized communities may lack the resources to cope effectively.
Long-term Implications and Recommendations
The implications of these findings extend beyond immediate health concerns. The study suggests that more unpredictable weather patterns can disrupt agriculture, water supply, and energy systems, creating a cascade of challenges for societies globally.
To mitigate these risks, the researchers recommend that governments and policymakers prioritize climate resilience strategies. This includes investing in infrastructure that can withstand temperature fluctuations, enhancing public health preparedness, and implementing early warning systems for extreme weather events.
As the effects of global warming continue to manifest, understanding and adapting to the new climate realities will be crucial. The findings of this study serve as a call to action for stakeholders at all levels to address the urgent challenges posed by climate-induced temperature variability.
In summary, the growing volatility in day-to-day temperatures underscores a pressing need for comprehensive climate action and public health planning. As the world grapples with these changes, it is imperative to prioritize the health of populations and the stability of essential services in the face of an uncertain climate future.