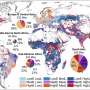
A new study published in Nature Climate Change provides the most detailed map of agricultural emissions to date, offering a critical tool for policymakers and communities aiming to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from farming. This research highlights the necessity of identifying emissions sources at a granular level, focusing not just on countries but also on specific crops and individual fields.
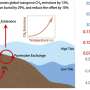
Through a comprehensive synthesis of data from various ground sources and models, researchers have achieved high-resolution mapping of global cropland emissions, revealing details down to approximately 10 kilometers. This approach allows for a breakdown of emissions by both crop type and source, pinpointing regions that require targeted mitigation efforts.
Understanding the specific emissions associated with different crops is essential. The study indicates that agricultural practices contribute significantly to global emissions, and without precise data, efforts to reduce these emissions could be misdirected. By identifying hotspots—areas with the highest emissions—policymakers can focus their strategies more effectively.
The research team, composed of experts in climate science and agriculture, employed advanced modeling techniques and extensive datasets to create this map. They emphasize that reducing emissions in agriculture is not just a matter of broad policies but requires localized actions tailored to the unique conditions of each region and crop.
Reducing agricultural emissions is critical in the fight against climate change. According to the researchers, the agricultural sector accounts for nearly a quarter of global greenhouse gas emissions. Recognizing the diverse sources of these emissions enables targeted interventions, which could lead to more sustainable farming practices and significantly lower emissions overall.
The findings underscore the importance of collaboration between scientists, policymakers, and farmers. Implementing the insights from this study could pave the way for innovative solutions that enhance food security while minimizing environmental impact. As countries strive to meet international climate commitments, such detailed mapping will be invaluable.
In summary, the research provides a vital step toward quantifying and reducing agricultural emissions. With this knowledge, stakeholders can develop more effective strategies to mitigate climate change, ensuring that agricultural practices align with global sustainability goals.