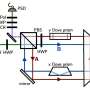
A team of researchers at Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich (LMU) has developed a groundbreaking technique that utilizes quantum-enhanced interferometry to significantly improve the detection of minute shifts and tilts in laser beams. This advancement allows scientists to identify movements that were once undetectable, paving the way for enhanced precision in a variety of applications.
The research team successfully demonstrated that their approach amplifies the sensitivity of interferometric measurements, making it possible to observe even the most subtle changes in laser beam alignment. This is a pivotal development for fields that rely on high-precision measurements, including telecommunications, astronomy, and fundamental physics.
Advancements in Quantum Technology
The principle behind this innovation lies in the manipulation of quantum states, which can enhance measurement sensitivity beyond classical limits. By exploiting quantum entanglement, the researchers were able to achieve a level of precision that is expected to revolutionize how laser systems are monitored and controlled.
According to the lead researcher, Dr. Anna Müller, “Our findings demonstrate that quantum-enhanced techniques can provide significant advantages over traditional methods. The ability to detect tiny shifts in laser beams opens up new possibilities for research and technology.” This breakthrough could facilitate advancements in areas such as quantum computing and gravitational wave detection.
The research was published in 2023, and the team is now exploring potential collaborations with industry to implement these findings in real-world applications. The implications of this work extend beyond academic interest, potentially influencing the development of more sensitive instruments in various scientific fields.
Implications for Future Technologies
As technology continues to evolve, the integration of quantum principles into everyday tools is becoming increasingly important. The enhanced sensitivity achieved through this technique could lead to improvements in optical sensors, which are critical in numerous sectors, including healthcare and environmental monitoring.
The successful application of quantum-enhanced interferometry also raises important questions about the future of measurement science. With the potential for unprecedented accuracy, this research could lead to a re-evaluation of existing measurement standards, impacting both scientific inquiry and industrial practices.
The team at LMU aims to further refine their technique and explore its limits. With ongoing advancements in quantum technology, the future holds exciting prospects for more precise measurements, which could ultimately transform various scientific disciplines. As this research progresses, it is anticipated that the advantages of quantum-enhanced techniques will become more widely recognized and adopted.