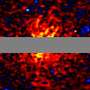
Scientists may have made a groundbreaking discovery in the field of astrophysics, potentially providing the first direct evidence of dark matter. Using data from NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope, researchers believe they have identified signs of this elusive substance, which has remained largely theoretical since its inception in the early 20th century.
Dark Matter’s Historical Context
The concept of dark matter originated in the early 1930s when Swiss astronomer Fritz Zwicky studied the movement of galaxies within the Coma Cluster. He noted that the galaxies were moving significantly faster than would be expected based on their visible mass. Zwicky proposed that some form of invisible matter, which he termed “dark matter,” must exist to account for this discrepancy. His theory has long been the foundation for contemporary astrophysical research.
Since Zwicky’s initial observations, scientists have searched for tangible evidence of dark matter, which is estimated to constitute approximately 27% of the universe’s total mass-energy content. Despite its significance, dark matter cannot be observed directly, as it does not emit, absorb, or reflect light. Instead, it interacts with visible matter through gravity.
New Findings from NASA
The recent findings from the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope mark a notable advancement in this ongoing quest. Scientists analyzed data regarding the distribution and behavior of gamma rays emitted from various cosmic sources. They discovered anomalies that suggest the presence of dark matter particles, which could be interacting with the surrounding matter in previously unobserved ways.
This revelation could transform our understanding of the universe. If confirmed, it would not only validate Zwicky’s early theories but also provide a clearer picture of how galaxies form and evolve. The data collected by the Fermi Telescope may shed light on dark matter’s role in shaping cosmic structures, thereby enhancing our comprehension of the universe’s composition.
While the findings are still undergoing rigorous scrutiny and require further validation, the potential implications are profound. If scientists can confirm the existence of dark matter through this evidence, it could open new avenues for research in cosmology and particle physics, prompting a reevaluation of existing theories.
The pursuit of understanding dark matter has been a collaborative effort among astronomers, physicists, and researchers worldwide. As technology advances, tools like the Fermi Telescope continue to play a crucial role in expanding our knowledge of the universe and its fundamental components.
In summary, the detection of potential dark matter particles by NASA’s Fermi telescope represents a significant milestone in astrophysics. As researchers continue to analyze and interpret this data, the scientific community remains hopeful that these findings will lead to a deeper understanding of one of the universe’s greatest mysteries.