Recent advancements in technology have led to a breakthrough in environmental conservation efforts. A study published in *Biology Methods and Protocols* reveals that a new deep-learning tool can effectively differentiate between wild and farmed salmon. This development has the potential to enhance strategies aimed at protecting natural ecosystems.
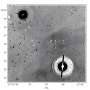
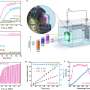
The research, titled “Identifying escaped farmed salmon from fish scales using deep learning,” was conducted by a team at the University of California, Santa Cruz. The study underscores the growing importance of utilizing artificial intelligence in ecological monitoring. By analyzing the unique characteristics of fish scales, the tool can accurately identify whether a salmon is wild or has been raised in captivity.
Impact on Environmental Strategies
The implications of this technology are significant. According to the researchers, identifying escaped farmed salmon is crucial for maintaining the health of wild populations. Farmed salmon often interbreed with wild fish, leading to genetic dilution and other ecological challenges.
The deep-learning model was trained on a diverse dataset of fish scale images, allowing it to recognize subtle differences that the human eye might miss. This precision could improve management practices for salmon fisheries and contribute to more sustainable fishing regulations globally.
Broader Applications in Conservation
Beyond salmon, the methodology developed in this study could be adapted for other species facing similar threats from aquaculture. The researchers believe that this tool could be instrumental in monitoring biodiversity and preventing the spread of non-native species in natural habitats.
As environmental concerns continue to grow globally, the integration of deep learning into conservation efforts represents a promising avenue for addressing complex ecological issues. This research not only highlights the interplay between technology and environmental science but also paves the way for future innovations in wildlife management.
The team encourages further collaboration among scientists, policymakers, and industry stakeholders to leverage this technology effectively. As the world grapples with the impact of climate change and habitat loss, tools like these could play an essential role in safeguarding our planet’s biodiversity.