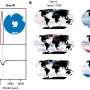
Recent research indicates that the melting of polar ice may inadvertently affect the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), a crucial system responsible for redistributing heat and nutrients across the Atlantic Ocean. This system, vital for regulating global climate, is approaching a critical threshold that, once crossed, could lead to significant and irreversible climate shifts.
Understanding the implications of the AMOC’s stability is essential. According to a report from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), this current system plays a key role in the climate balance, influencing weather patterns across Europe, North America, and Africa. The AMOC transports warm water from the tropics to the North Atlantic, impacting temperatures and precipitation patterns.
Potential Consequences of AMOC Disruption
Research suggests that continued polar ice melt could destabilize the AMOC, prompting a series of rapid climate changes. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has highlighted that even slight alterations in the AMOC could lead to dramatic shifts in weather patterns, including more intense storms, prolonged droughts, and rising sea levels.
The Arctic region, which has experienced some of the fastest rates of warming globally, is pivotal in this equation. As ice melts, the influx of freshwater into the North Atlantic could disrupt the natural salinity levels necessary for maintaining the AMOC’s flow. A study published in March 2024 emphasizes that if the AMOC were to collapse, the consequences could extend far beyond the Atlantic, affecting global climate systems.
Addressing the Challenge
Experts emphasize the urgency of mitigating climate change to prevent the AMOC from reaching a tipping point. The melting of polar ice, while presenting a potential solution to water scarcity in some areas, poses significant risks to global climate stability.
It is essential for policymakers to integrate findings from climate research into strategic planning. Investment in renewable energy and sustainable practices can help lower greenhouse gas emissions, which are driving climate change. According to NOAA, immediate action is necessary to prevent further disruption to the AMOC and other climate systems.
As the world grapples with the implications of climate change, the situation highlights the interconnectedness of environmental systems. The melting polar ice, while presenting challenges, also serves as a stark reminder of the need for collective global action. The time to act is now, as the consequences of inaction could reverberate across the planet for generations to come.