As the winter months in the United Kingdom see diminishing sunlight, many individuals are turning to vitamin D supplements to fend off seasonal illnesses and low moods. Health experts, however, are sounding alarms about the potential side effects associated with improper usage of these supplements.
Vitamin D, often referred to as the “sunshine vitamin,” is produced by the body through sunlight exposure. It is also found in certain foods like oily fish, red meat, and egg yolks. This vitamin plays a critical role in regulating calcium and phosphate levels, which are essential for maintaining healthy bones, teeth, and muscles. Yet, with daylight hours significantly reduced in winter, approximately one in six people in the UK have vitamin D levels that fall below government recommendations.
The National Health Service (NHS) advises that from October to March, it is challenging to generate sufficient vitamin D from sunlight. To maintain bone and muscle health, the NHS recommends a daily supplement of 10 micrograms of vitamin D, available from pharmacies and retailers.
Dr. Kathryn Basford, a healthcare professional at Asda Online Doctor, noted, “Everyone in the UK can benefit from taking vitamin D during the darker months. Although dietary sources can contribute to our vitamin D intake, it is often insufficient.” She highlighted that insufficient vitamin D levels can lead to symptoms such as fatigue, muscle pain, and recurrent infections.
While Dr. Basford stated that vitamin D is generally safe when taken as prescribed, she cautioned against excessive intake. “Overconsumption of fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K can lead to accumulation in the body, resulting in toxicity,” she explained.
Recognizing Symptoms and Dosage
Common side effects of excessive vitamin D intake include nausea, headaches, and fatigue. Dr. Basford emphasized that anyone experiencing these symptoms should consult their doctor to ensure they are taking the appropriate dosage.
Katherine Elyse Blake, a qualified nutritionist and women’s health consultant, pointed out that vitamin D needs can vary greatly based on several factors, including sun exposure, skin tone, body weight, diet, age, and pre-existing health conditions. “A dose suitable for one individual may be excessive for another,” she said.
Moreover, timing can influence the effectiveness of vitamin D supplements. Taking them late in the day may disrupt sleep patterns for some individuals, as it can affect melatonin production. “It is generally better to take vitamin D earlier in the day, ideally with a meal that contains fat for better absorption,” Blake advised.
Dr. Aiza Jamil, a consultant dermatologist, also warned about the implications of incorrect vitamin D intake on skin health. She explained that vitamin D is vital for maintaining skin structure and health and that improper absorption can lead to issues such as dryness and an impaired skin barrier. “Vitamin D regulates keratinocyte differentiation and lipid production, which are crucial for skin health,” she stated.
Choosing the Right Supplement Form
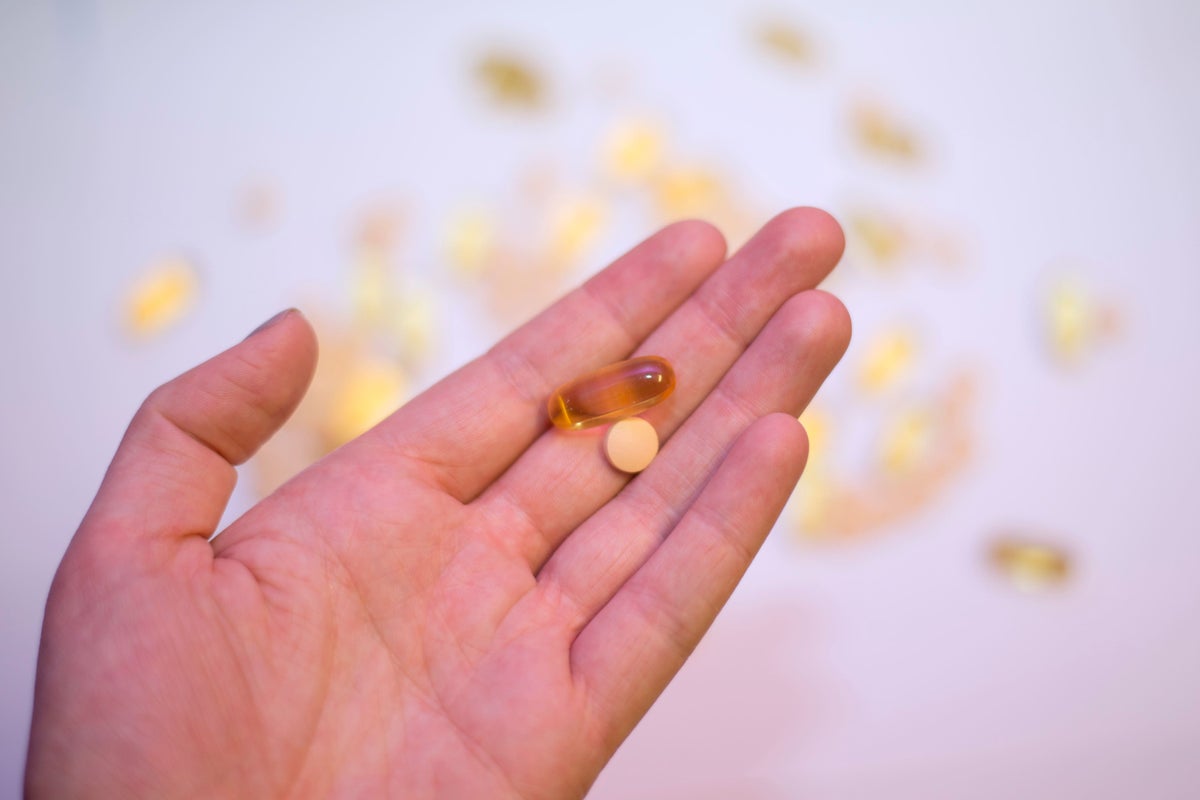
When considering vitamin D supplements, there are various forms available on the market. Dr. Basford mentioned that tablets are the most common but may take longer to absorb since they must be broken down in the digestive system.
Conversely, oral sprays provide quicker absorption as they deliver nutrients directly into the bloodstream through the mouth. However, users should be cautious about added sugars or artificial flavors and choose reputable brands. Gummies are another option, often preferred for their taste, but they may contain added sugars and have lower nutrient density compared to tablets.
Correct use of vitamin D supplements can undoubtedly offer significant health benefits, especially during the winter months. As individuals consider their options, it is essential to approach supplementation with informed caution, ensuring they adhere to recommended guidelines for safe and effective usage.