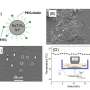
A team of researchers at Boston College has made a significant breakthrough in immunology by demonstrating how ultrasound-activated piezoelectric nanoparticles can stimulate an inflammatory response within immune cells. This innovative approach could enhance the body’s ability to combat diseases more effectively.
The researchers focused on the potential of these nanoparticles to be deployed inside immune cells, where they can be remotely activated using ultrasound technology. This method allows for a targeted response, potentially revolutionizing how treatments for various diseases are administered. The study emphasizes the capacity of these nanoparticles to harness the body’s natural defenses, making the treatment more efficient.
Mechanism of Action
The nanoparticles operate on a simple yet effective principle. When activated by ultrasound, they generate mechanical forces that can trigger a cascade of biological reactions within the immune cells. This process induces the cells to produce signaling molecules that promote inflammation, a crucial aspect of the immune response.
According to the research team, this technique could open new avenues for therapies aimed at conditions where the immune response is either insufficient or misdirected. By precisely controlling the activation of these nanoparticles, clinicians could potentially tailor treatments to individual patients, enhancing therapeutic outcomes.
The cross-disciplinary nature of this research highlights the collaboration between experts in biomedical engineering, immunology, and materials science. The team aims to further explore the implications of their findings, especially in the context of chronic diseases that involve dysregulated immune responses.
Future Implications
The potential applications of ultrasound-activated nanoparticles extend beyond just inflammation. Researchers believe that this technology could be adapted for various therapeutic strategies, including cancer treatment and autoimmune disorders.
The study, published recently in a leading scientific journal, underscores the importance of innovation in developing new medical therapies. As researchers continue to refine this technology, it may lead to significant advancements in how diseases are treated, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
With ongoing trials and research, the team at Boston College is optimistic about the future of this technology. The integration of ultrasound with nanoparticle technology could provide a non-invasive option for enhancing the immune response, potentially changing the landscape of medical treatment as we know it.
As the research progresses, the broader medical community is watching closely for updates, eager to see how these findings will translate into practical applications for patients worldwide.