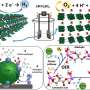
Researchers at the University of California have developed a groundbreaking catalyst that significantly enhances the efficiency of green hydrogen production through water electrolysis. This new molecular switch alters its function based on its assembly, presenting a promising alternative to the precious metals currently used in the industry, such as iridium and platinum.
Hydrogen production is pivotal in the transition to clean energy, particularly as countries strive to reduce carbon emissions. Traditional methods of water electrolysis require stable and efficient catalysts that typically operate under acidic conditions. The reliance on expensive metals has limited the scalability of hydrogen technologies.
The newly developed catalyst showcases a remarkable ability to adapt according to its structural configuration. This adaptability not only enhances performance but also reduces the overall cost of hydrogen production. The team’s findings were published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society in 2023, highlighting the potential for broader application in renewable energy systems.
Innovative Approach to Catalysis
The researchers focused on creating a catalyst that could maintain high activity levels without the drawbacks associated with traditional materials. By manipulating the assembly of the catalyst’s molecular structure, they achieved a switch-like function that optimizes its performance based on the environment in which it operates.
This innovative approach addresses critical challenges in current hydrogen production methods, particularly the need for sustainable and cost-effective solutions. The team noted that by reducing dependence on precious metals, the production process could become much more accessible and economically viable.
The implications of this advancement could extend far beyond hydrogen production. If scaled effectively, this technology could contribute significantly to the global shift towards renewable energy sources. As countries invest heavily in green technologies, the demand for efficient catalysts is expected to grow.
Path Forward for Green Energy
As the world faces the urgent need for cleaner energy solutions, the development of this catalyst represents a significant stride towards a sustainable future. The ability to produce hydrogen more efficiently could play a key role in various sectors, including transportation, manufacturing, and energy storage.
The research team emphasizes the importance of further studies to fully understand the long-term stability and scalability of this new catalyst. Future projects will focus on refining the assembly process and testing the catalyst in real-world conditions.
Overall, this breakthrough positions the University of California at the forefront of green hydrogen research. By offering a practical solution to one of the industry’s most pressing challenges, the researchers are contributing to a cleaner, more sustainable energy landscape. As the clean energy transition continues to gain momentum, innovations like this catalyst will be essential in meeting global energy demands while reducing environmental impact.